Is Ram Compatible With All Motherboards? – Full Guide 2026
Upgrading your computer’s memory may seem straightforward, but assuming all RAM modules are interchangeable can lead to costly mistakes. RAM compatibility depends on a combination of physical design, electrical standards, and firmware support.
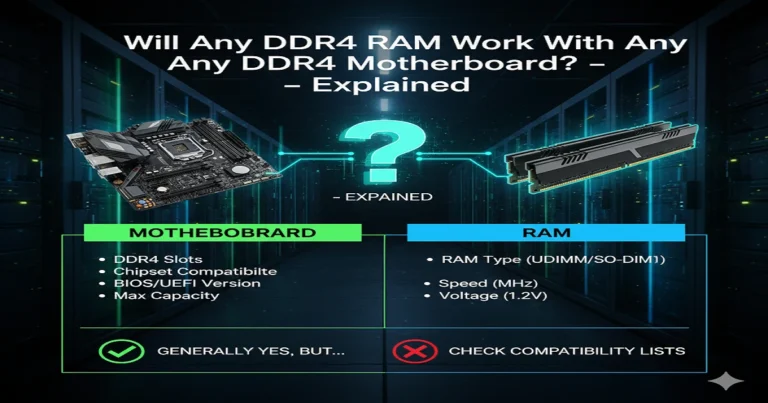
Many people ask, “Is RAM compatible with all motherboards?” when they want to upgrade their computer. The simple answer is no. Not all RAM works with every motherboard because each board supports specific RAM types, speeds, and maximum sizes. Choosing the wrong RAM can make your PC fail to start or run slowly. In this guide, I will explain in easy steps how to check your motherboard’s RAM compatibility. You will learn how to read specifications, find the correct RAM type, and pick memory that fits perfectly, keeping your computer safe, fast, and trouble-free.
What RAM Compatibility Actually Means
RAM compatibility ensures your motherboard can recognise, power, and communicate with the memory modules installed. Every motherboard has a memory controller, either integrated into the CPU or chipset, which dictates the supported DDR generation, module density, and memory speed.
For a deeper understanding of how motherboards manage memory and peripherals, check out motherboard components and functions.
Why Not All RAM Fits All Motherboards
The RAM slot on your motherboard is not universal. Each DDR generation (DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5) has unique notch positions, pin layouts, voltage requirements, and signalling protocols. This prevents incorrect installation and ensures electrical compatibility.
RAM Generations and Physical Differences
| Generation | Year Introduced | Pin Count (DIMM) | Voltage | Compatible Boards |
| DDR3 | 2007 | 240 | 1.5V | DDR3-only boards |
| DDR4 | 2014 | 288 | 1.2V | DDR4 boards |
| DDR5 | 2020 | 288 | 1.1V | DDR5 boards |
Why These Differences Exist
Each generation moves the key notch to prevent physical mismatch. Even if DDR4 and DDR5 share 288 pins, they cannot fit each other’s slots.
For an overview of motherboard architecture and memory channels, see What is a motherboard.
The Motherboard’s Role in RAM Compatibility
The motherboard acts as the central hub for CPU, RAM, GPU, and storage communication. It defines maximum memory capacity, supported DDR type, voltage, and frequency ranges.
Learn more about motherboard types and chipsets here: What are motherboards?
Chipset Limitations
Chipsets like Intel B660 or AMD X670 define the supported memory speeds, dual-channel or quad-channel configuration, and maximum RAM per slot.
BIOS and Firmware Factors
A BIOS update can improve memory compatibility, stability at higher speeds, and support for new RAM modules—but cannot change DDR generation.
Form Factor Matters: DIMM vs SODIMM
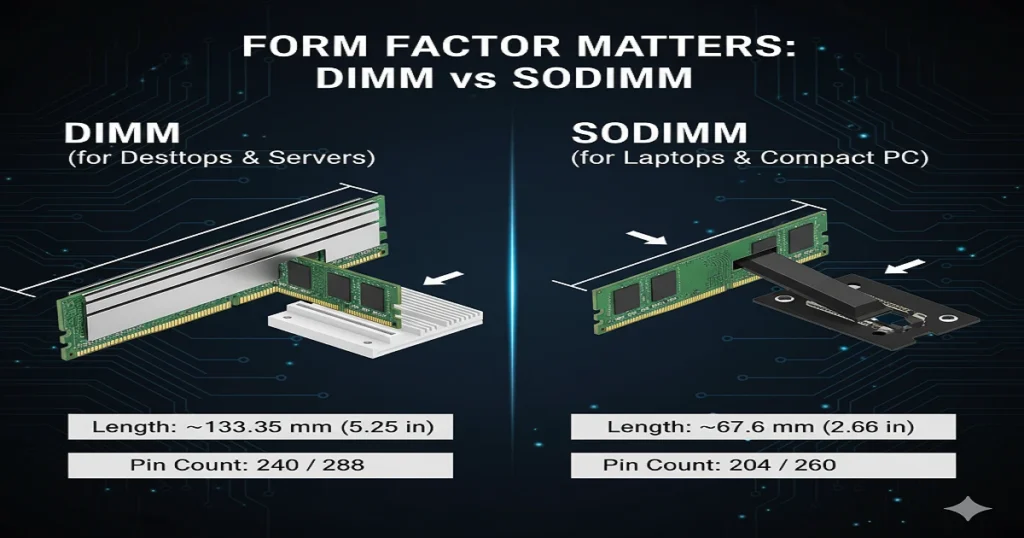
Desktop and laptop RAM are physically incompatible.
- DIMM: Standard desktop modules with a larger pin count.
- SODIMM: Compact modules for laptops.
For a detailed comparison of motherboard slot layouts, see Is baseboard the same as motherboard?.
Electrical and Voltage Compatibility
Voltage mismatch can prevent booting or cause system instability.
| RAM Type | Typical Voltage |
| DDR3 | 1.5V |
| DDR4 | 1.2V |
| DDR5 | 1.1V |
DDR5’s Power Regulation Change
DDR5 modules include on-module power management (PMIC), reducing motherboard dependency for voltage regulation.
The Role of CPU in Memory Compatibility
Even if your motherboard supports DDR5, your CPU must support it. Modern processors include an integrated memory controller (IMC), which dictates RAM compatibility.
Intel and AMD Example:
- Intel 12th/13th Gen CPUs can work with DDR4 or DDR5, depending on the motherboard variant.
- The AMD Ryzen 7000 series supports DDR5 only, while the Ryzen 5000 supports DDR4.
RAM Speed and Frequency Limits
Your motherboard specifies the maximum RAM frequency. Faster RAM will downclock to the motherboard’s highest supported speed.
Example: A DDR4-4000 MHz kit will run at 3200 MHz if the board only supports 3200 MHz.
Using XMP or EXPO Profiles
Enabling Intel XMP or AMD EXPO in BIOS allows RAM to run at advertised speeds, improving system performance.
For detailed instructions, see how to check what RAM is compatible with my motherboard.
How to Find Out What RAM Your Motherboard Supports
- Locate your motherboard model.
- Visit official brand support → Specifications → Memory (QVL).
- Use online tools: Crucial Scanner, Corsair Memory Finder, and Kingston Configurator.
- More guidance: What RAM will my motherboard support?
Common Compatibility Mistakes
- Mixing DDR4 and DDR5.
- Combining different speeds or voltages.
- Using SODIMM in desktop boards.
- Ignoring BIOS updates before upgrades.
What Happens If You Use the Wrong RAM
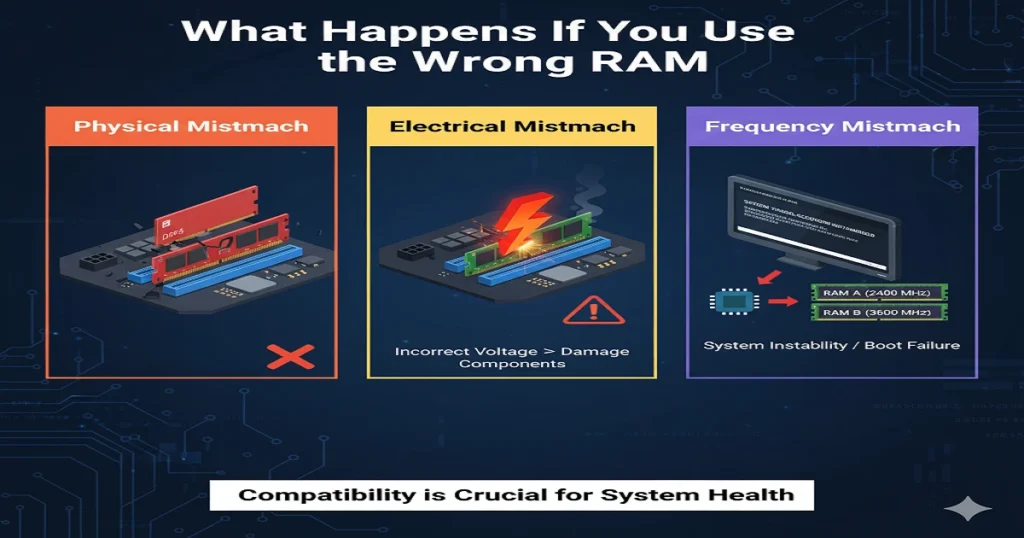
Physical Mismatch
The RAM module won’t fit into the slot.
Electrical Mismatch
Voltage differences may prevent startup.
Frequency Mismatch
The system may boot but suffer instability, crashes, or reduced performance.
ECC, Buffered, and Non-ECC RAM
- Workstation motherboards often support ECC RAM for error detection and correction.
- Consumer boards generally support non-ECC RAM.
When ECC Makes Sense
Critical workloads like servers, databases, or scientific computing benefit from ECC.
The Future of RAM Compatibility
DDR6 is expected after 2026 with higher bandwidth and efficiency but zero backward compatibility.
Transition Boards
Hybrid platforms (e.g., Intel B660 DDR4 & DDR5 variants) help users upgrade gradually.
BIOS Updates and Stability Improvements
BIOS updates can:
- Improve boot success with new RAM
- Support higher memory frequencies
- Stabilize voltage for overclocked modules
Safe Update Practices
Follow the motherboard manufacturer’s instructions when flashing BIOS to prevent corruption or failure.
FAQs
How do I know if my RAM is compatible with my motherboard?
To check RAM compatibility, make sure the following match:
The RAM type must match (most important!)
Your motherboard supports only one DDR generation:
- DDR3
- DDR4
- DDR5
You must use the same type.
They are not cross-compatible.
The speed must be supported
Example:
If the motherboard supports 2400 MHz and your RAM is 3200 MHz, the RAM will run at 2400 MHz.
The capacity must be supported
Check your board’s manual for:
- Maximum RAM total (e.g., 32GB, 64GB, 128GB)
- Maximum per slot (e.g., 16GB per slot)
ECC vs Non-ECC
- Consumer motherboards usually support non-ECC RAM.
- ECC RAM works only on motherboards that explicitly support it.
Laptop vs Desktop RAM
- Desktop RAM = DIMM
- Laptop RAM = SO-DIMM
They are NOT interchangeable.
Does all RAM fit into all motherboards?
No.
RAM must match the exact DDR type of the motherboard.
Example
- DDR4 RAM does not fit in a DDR3 slot (different notch position).
- DDR5 RAM does not fit in a DDR4 slot.
- Laptop RAM does not fit in desktop motherboards.
Only RAM of the same DDR generation and physical size works.
Can I put 3200 MHz RAM in a 2400 MHz motherboard?
Yes, as long as it is the correct DDR type.
The RAM will simply run at 2400 MHz, the maximum speed the motherboard supports.
It will:
✔ Work
✔ Be safe
✔ Automatically downclock
✘ Not run at 3200 MHz
How do I know if my motherboard is DDR3 or DDR4?
Use any of these methods:
Method 1: Check the motherboard model
- Find the model printed on the motherboard (e.g., “ASUS B450M-A”).
- Search the model’s specifications online.
- Look for memory/RAM type → will say DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5.
Method 2: Check your installed RAM
Use CPU-Z (free tool):
- Open CPU-Z
- Go to Memory tab
- Look for “Type”.
- DDR3
- DDR4
- DDR5
Method 3: Physical clues
- DDR3 and DDR4 have different notch positions.
- DDR4 modules have slightly curved edges on the bottom.
- The label on RAM sticks usually says “DDR3” or “DDR4”.
Method 4: Task Manager (indirect)
Windows doesn’t show DDR type directly, but speeds can help:
- 1066–1600 MHz → usually DDR3
- 2133–3200+ MHz → usually DDR4
Conclusion:
RAM is not universal. Every motherboard supports specific DDR generations, module density, voltage, and speeds. Installing incompatible RAM can cause boot loops, crashes, and wasted money. Choosing the right RAM for your motherboard is crucial for system stability, performance, and longevity. Not all RAM is compatible with the DDR generation; module type (DIMM vs SODIMM), voltage, frequency, and CAS latency all play a role. Installing incompatible memory can cause boot failures, crashes, or reduced performance. Always check your motherboard’s QVL (Qualified Vendor List), use verified tools like CPU-Z or Crucial System Scanner, and enable XMP/EXPO profiles for optimal performance. Planning carefully ensures your upgrade is smooth, maximises multitasking, gaming, and professional workloads, and effectively future-proofs your system.