Motherboard Components and Functions – Ultimate Guide (2026)
A motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and powers all computer components. Its key components include the CPU socket, RAM slots, chipset, BIOS, and expansion slots, each working together to manage data flow and system functions efficiently.
Learn about the main parts of a motherboard and what each part does to make your computer work.
What Is a Motherboard and Why Does It Matter
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It connects every major component from the CPU to RAM, allowing them to communicate smoothly. Think of it as the computer’s nervous system, linking each part through data pathways and power channels.
Without a motherboards Features, your computer couldn’t function. It distributes electricity, manages signals, and ensures that hardware components, such as storage drives and expansion slots, work together effectively. Learn more about what a motherboard does at TechQuills.
Evolution and History of Motherboards
Early motherboards from IBM were simple circuit boards. Over time, they evolved into the complex, multilayered PCBs we see today. Each new form factor, like ATX and Micro-ATX, brought better design, efficiency, and power control.
The shift from BIOS to UEFI firmware also transformed how computers boot and store system settings. Today’s motherboards even support AI-powered diagnostics for automatic troubleshooting.
Types of Motherboards (Form Factors and Standards)
Different form factors fit various computer needs. ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX boards are common in desktops. eATX and Flex ATX serve high-end or compact setups. Each type affects performance, cooling, and upgrade flexibility.
Smaller boards like Mini-ITX are ideal for gaming PCs or AI workstations where space is limited. Larger eATX boards offer extra PCIe slots and more power connectors for advanced builds.
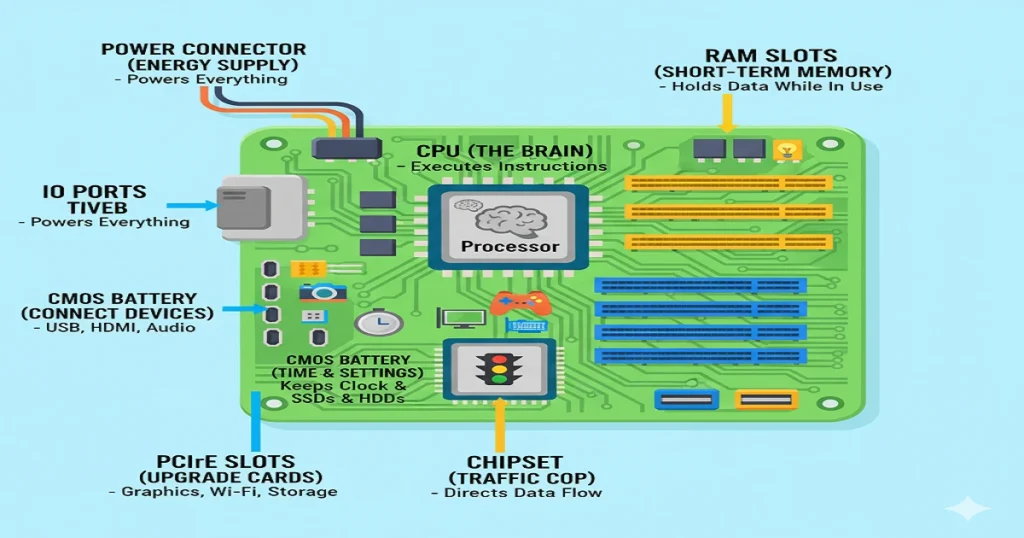
Key Components of a Motherboard (2026 Breakdown)
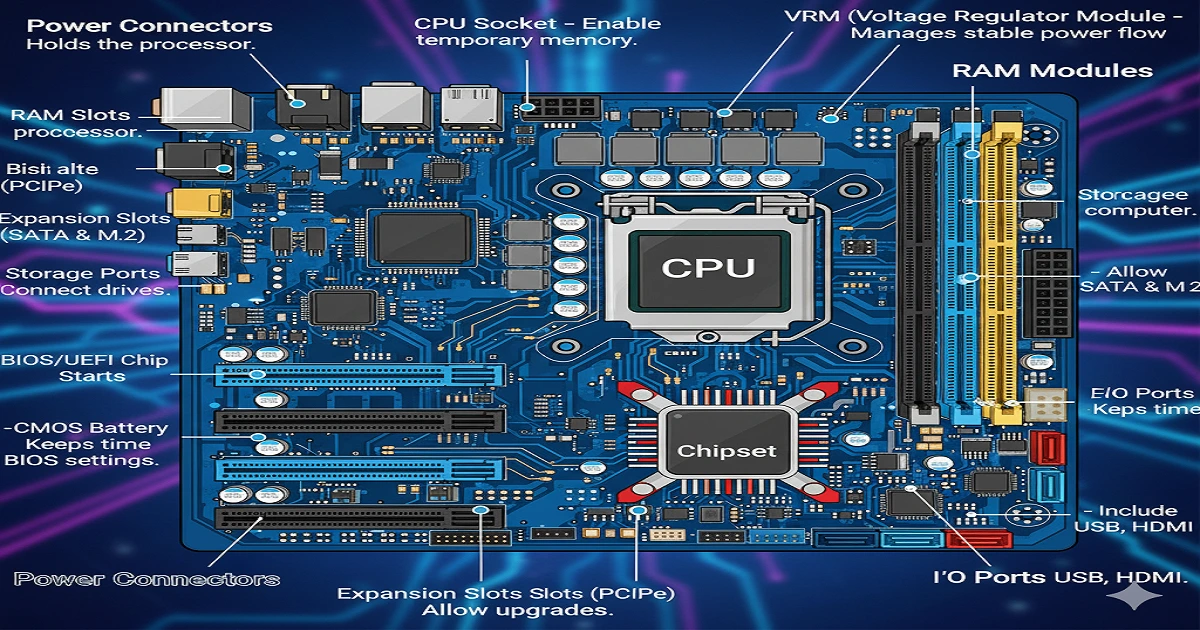
Every motherboard houses several vital parts that keep your system running efficiently:
- CPU Socket – Holds the processor. Modern sockets like LGA 1851 and AM6 support next-gen CPUs.
- Chipset – The motherboard’s traffic cop, directing communication between CPU, RAM, and storage.
- RAM Slots – Enable temporary memory. Newer boards support DDR5 and even DDR6 memory.
- VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) – Manages stable power flow.
- Expansion Slots (PCIe 6.0/7.0) – Allow upgrades like graphics cards or AI accelerators.
- Storage Ports (SATA & M.2) – Connect HDDs, SSDs, and NVMe drives.
- BIOS/UEFI Chip – Starts the computer and runs basic system tests.
- CMOS Battery – Keeps time and BIOS settings.
- Power Connectors – Supply power to the CPU and motherboard.
- I/O Ports – Include USB4, Thunderbolt 5, and HDMI.
CPU Socket – The Brain’s Home
The CPU socket determines which processors fit your motherboard. Intel’s LGA 1851 and AMD’s AM6 lead the 2026 lineup. Always check compatibility when upgrading. Proper cooling and power phases improve performance and lifespan.
Chipset – The Control Center
Your chipset defines your PC’s abilities. Advanced models like Intel Z890 or AMD X970 support faster PCIe lanes, overclocking, and AI acceleration. It manages data flow between components and decides what features your system can use.
RAM Slots – System Memory Power
RAM slots allow your computer to store data it’s using right now. In 2026, DDR6 offers lightning-fast speed and efficiency. More RAM capacity means smoother multitasking and faster performance, especially in gaming and design tasks.
Power Connectors and VRM
The ATX 24-pin connector powers the motherboard, while VRMs ensure a clean, stable voltage. Modern designs use up to 20 power phases for better CPU control. This helps prevent overheating and improves long-term reliability.
Expansion Slots (PCIe and Beyond)
PCIe 6.0 and PCIe 7.0 offer extreme data speeds for GPUs, SSDs, and AI accelerators. Some boards even support external GPU (eGPU) setups for creative professionals and gamers.
Storage Connectors (SATA and M.2)
Modern boards feature both SATA and M.2 NVMe slots. M.2 drives deliver up to four times faster speeds than traditional HDDs. For high-end users, RAID setups enhance performance and data protection.
BIOS and UEFI Firmware
UEFI replaced the old BIOS, adding better security and user-friendly interfaces. Features like BIOS Flashback let you update without a CPU installed. It’s the first software your system runs when powering up.
CMOS Battery
This small battery saves system time and settings. If your PC forgets the date or boot order, replacing it fixes the issue. It’s simple but vital for stability.
Input/Output Ports
Modern motherboards come packed with USB4, Thunderbolt 5, and WiFi 7 for blazing connectivity. Built-in Bluetooth 6 and 10G LAN keep your system fast and connected.
How Does a Motherboard Work?
A motherboard channels power and data between all parts. It connects your CPU, RAM, and storage through circuits on the PCB. When you press “power,” the BIOS wakes up the system, checks for problems, and then loads your operating system.
Motherboard Functions Explained
A motherboard has three main jobs: managing data flow, distributing power, and ensuring smooth communication. It also controls boot processes, improves performance, and provides a stable base for all connected devices.
Building or Upgrading a PC – Choosing the Right Motherboard
When upgrading, always check CPU socket, RAM type, and power needs. For future-proofing, pick boards with PCIe 7.0 and DDR6 support. Explore TechQuills’ Motherboard Guide to choose the best one for your build.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- No display? Check power connectors.
- Beep codes? Inspect RAM and CPU.
- BIOS not saving? Replace the CMOS battery.
- USB not working? Reset BIOS.
- System crashing? Look at VRM temperatures.
Sustainability and E-Waste Management
Modern boards meet RoHS and EPEAT standards. Recycle old boards properly; many contain copper and fiberglass that can be reused. Eco-friendly designs are shaping a greener computing future.
Future of Motherboards (2026–2030)
By 2030, expect AI-powered BIOS, quantum-ready boards, and smart diagnostics. Energy-efficient ATX12VO systems and AI workstations will redefine computing. The motherboard will stay the heart of innovation.
FAQs:
What are the 5 components of a motherboard?
The five main components are the CPU socket, RAM slots, chipset, expansion slots, and power connectors, which together enable system operation.
What are motherboard components and functions?
Motherboard components include the CPU, RAM, chipset, BIOS, and connectors, and their function is to link and coordinate all computer hardware efficiently.
What are the 7 main components of a computer system?
They are the CPU, motherboard, memory (RAM), storage drive, power supply, input devices, and output devices, forming a complete computing unit.
What are the 5 main components of a PC?
The five key PC components are the CPU, motherboard, memory, storage, and power supply, which handle processing, storage, and system control.
Conclusion
Understanding motherboard components and functions helps you build better systems and solve issues easily. As tech evolves, mastering these basics keeps your knowledge and your PC future-ready.