What Are Motherboards? Anatomy, Evolution, Features Guide
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in your computer—the central hub where CPU, RAM, GPU, storage, and ports connect. It distributes power from the PSU, routes data via buses, and manages communication for smooth, fast performance.
Ever wondered what holds your computer together? The motherboard is the main green circuit board – the “heart” of your PC! It’s where the CPU (brain), RAM (memory), GPU (graphics card), storage drives, and ports all connect.
It distributes power from the PSU, routes data super fast through buses, and makes sure everything talks smoothly for gaming, work, or AI tasks. Without it, your PC is just loose parts!
This 2026 guide breaks down parts, types, how it works, and buying tips. Perfect for beginners – read on for future-proofing!
Motherboard Fundamentals and Definition
Core Definition and Role in a PC
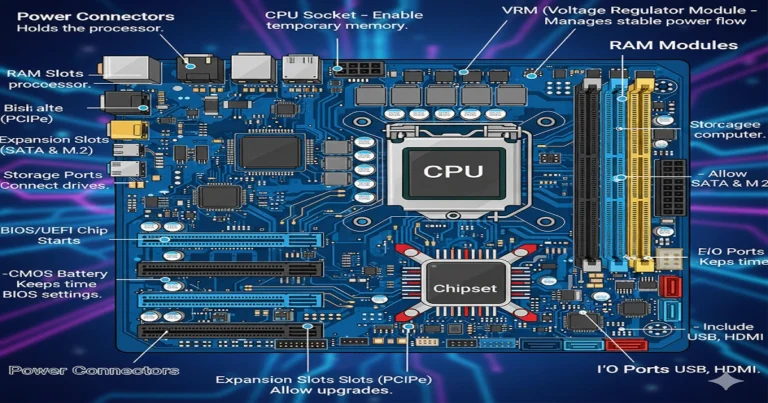
A motherboard is the largest, most complex printed circuit board (PCB) in your computer – the “master connector” that links CPU, RAM, GPU, storage, and peripherals. It’s not just a board; it’s the system’s “conductor”, routing power, data, and signals at billions of operations per second.
Role Breakdown Table
| Role | Simple Explanation | Real-World Benefit |
| Data Router | Moves info between parts (buses/lanes) | Smooth gaming (no lag) |
| Power Distributor | Shares electricity from PSU | Stable overclocking |
| Upgrade Enabler | Defines what you can add (slots/sockets) | Future-proof builds |
Materials and Construction Layers
Motherboards use 8-14 fibreglass layers with copper traces (thinner than hair – 35 microns wide). 2026 boards add carbon fibre for rigidity.
Layer Structure
- Top: Components (sockets, chips)
- Middle: Signal/power planes (ground for noise reduction)
- Bottom: Solder mask (green color)
Motherboard vs. Other Boards (Clarifying Confusion)
Comparison Table
| Board Type | Active Components | Upgradeable | Use Case |
| Motherboard | Chipset, BIOS | Yes | Desktops/laptops |
| Backplane | None | High | Servers (modular) |
| Daughterboard | Limited | No | Add-ons (Wi-Fi) |
Detailed Anatomy: Every Component Explored
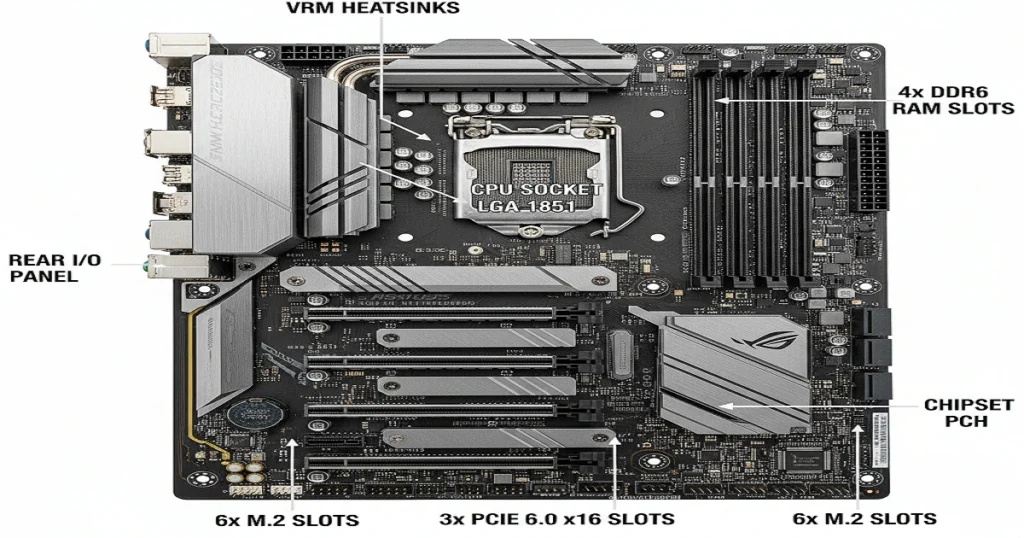
CPU Socket and VRM System
Sockets secure CPUs; VRMs provide clean power (1-1.4V).
2026 Socket Deep Specs
Pin Design – LGA (Land Grid Array): Flat pads on CPU, pins on board.
Compatibility – Check the BIOS version for compatibility with new CPUs.
VRM Evolution Table
| Year | Phases Avg | Amp Rating | Heat Output |
| 2025 | 20 | 90A | High |
| 2026 | 30+ | 140A | Low (AI cooled) |
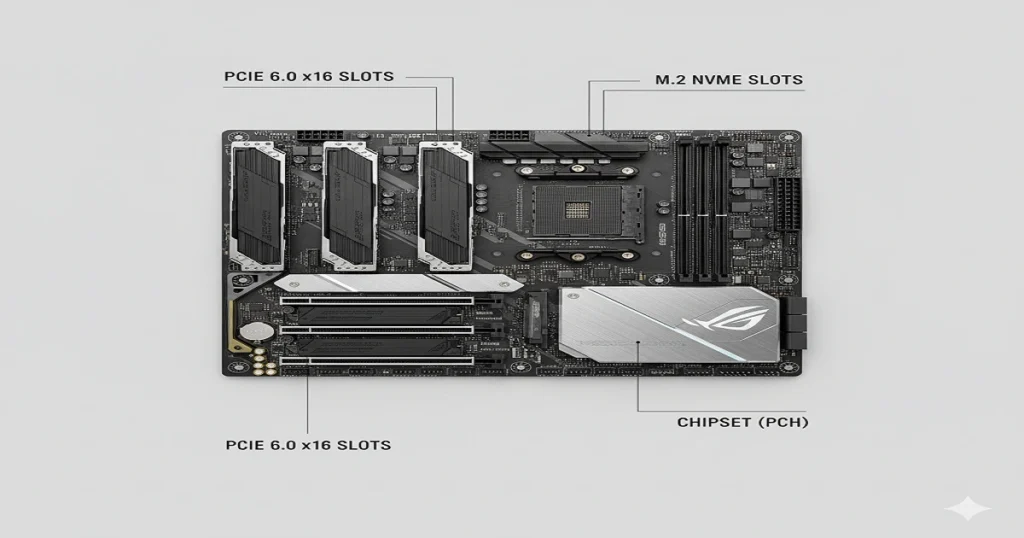
Memory Slots, PCIe, and M.2 Expansion
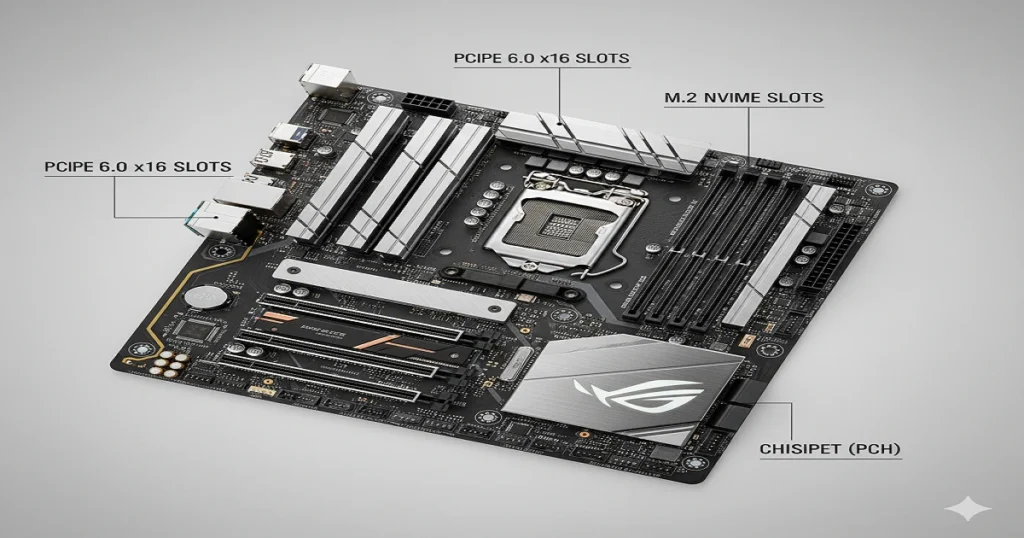

RAM slots (DIMM) for DDR6; PCIe for GPUs.
Expansion Bandwidth Table (2026)
| Slot Type | Lanes | Bandwidth (GB/s) | Max Devices |
| PCIe 6.0 x16 | 16 | 512 | 1 GPU |
| M.2 PCIe 6.0 | 4 | 128 | 6 SSDs |
Chipset and I/O Controllers
The chipset (PCH) manages 24+ lanes for USB/SATA.
Chipset Features
- DMI Link: 16 GT/s to CPU
- 2026: Integrated NPU (60 TOPS)
Evolution and Historical Milestones
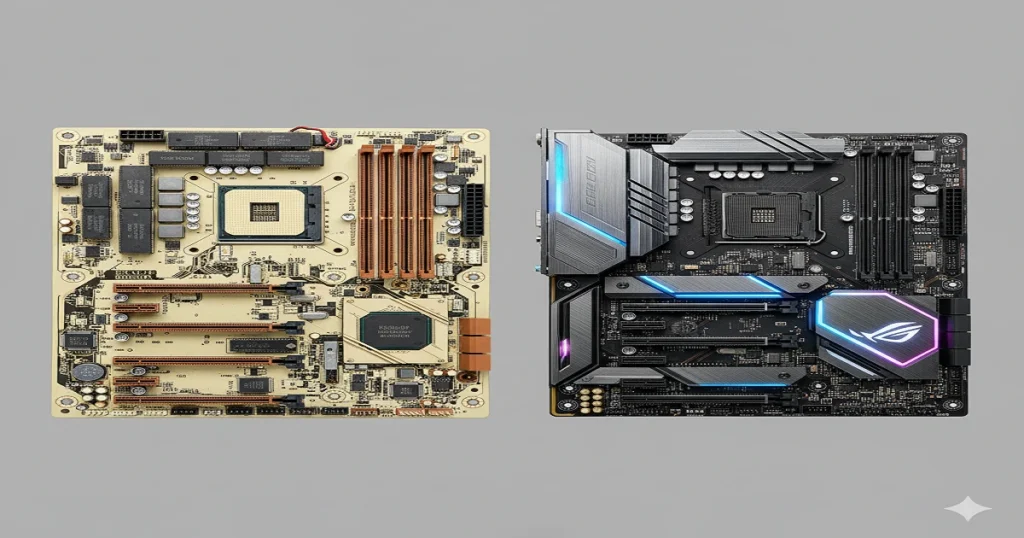
Pre-1990s Foundations
1970s backplanes evolved to the 1981 IBM AT (first socket).
Early vs Modern Table
| Era | Socket Type | Lanes Total |
| 1980s | PGA | 8 |
| 2026 | LGA/AM | 72 |
1990s-2020s Integration Wave
Super I/O chips added legacy ports; PCIe 1.0 (2004) was revolutionary.
2026 and Future Horizons
In 2026, the motherboard era PCIe 6.0 full consumer rollout and DDR7 preview (2027).
Future Tech Table
| Tech | 2026 Speed | 2027 Expectation |
| PCIe | 64 GT/s | 128 GT/s (7.0) |
| DDR | 25,600 MT/s | 51,200 MT/s |
Internal Functionality: Beyond Basic Boot
Advanced Boot Sequence
Pillar covered basics; here, DDR6 training (10s longer due to ECC).
POST Phases H3
Phase 1: CPU Init (0.2s)
Phase 2: RAM Train (5s)
Runtime Data and Resource Management
The chipset prioritises (e.g., GPU 75% lanes in games).
Prioritization Table
| Task | Lane Allocation % | Example |
| Gaming | 80 | GPU x16 |
| File Copy | 50 | SSD x4 |
Thermal and Power Optimization
20+ sensors; AI predicts loads (ASUS AI Cooling II).
Form Factors and Specialized Types
Standard Sizes Deep Comparison
ATX for balance; E-ATX for extremes.
Size Pros/Cons Table
| Form Factor | Pros | Cons |
| ATX | 4 RAM, 3 PCIe | Larger case needed |
| Mini-ITX | Compact | 2 RAM only |
Specialized Variants (Gaming, Server)
Gaming: Q-Flash BIOS. Server: Dual socket.
Variant Table
| Type | Extra Features | Cost Add-On |
| Gaming | RGB, 10G LAN | +$100 |
| Server | ECC RAM, IPMI | +$200 |
Selecting Form Factor for Your Build
Match case + needs (SFF? Mini-ITX).
Onboard Features and Modern Connectivity
Networking, Audio, and Wireless
Wi-Fi 7 multi-band (2.4/5/6 GHz).
Connectivity Table (2026)
| Feature | Speed | Ports Avg |
| Ethernet | 25G | 1 |
| Wi-Fi | 46 Gbps | 1 |
Security, AI, and Extras
TPM 2.2 + NPU for Windows 12 AI.
AI Features
- Auto OC: +500 MHz free
- Noise Cancel: Built-in mic AI
Ultimate Buying Guide for 2026
Budget Tiers and Value Picks
$100-150: Entry. $400+: Flagship.
Tier Table
| Tier | Price Range | VRM Phases | PCIe Gen |
| Budget | $100-200 | 14 | 5.0 |
| Premium | $400+ | 32 | 6.0 |
15 Must-Have Specs Checklist
- Socket match
VRM Quality
Phases >20 for OC - M.2 count (6+)
Top 10 2026 Recommendations
- ASUS ROG Crosshair X670E Hero ($599) – PCIe 6.0 king
Recommendations Table
| Board | Socket | Price | Standout Feature |
| Gigabyte Aorus X870 Elite | AM6 | $350 | 5 M.2 PCIe 6.0 |
Motherboard Myths Busted
Performance Myths
Myth: “More phases = always better.” Fact: Depends on amps (90A+ for 2026).
Myths Table
| Myth | Truth |
| “RGB means high-end.” | Cosmetic – ignore for power |
| “All Z-series overclock.” | Needs good VRM |
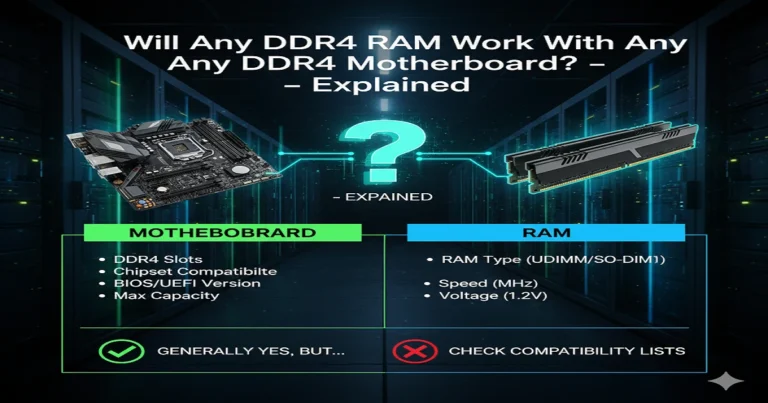
Compatibility Misconceptions
Myth: “BIOS update fixes all.” Fact: QVL list for RAM.
Advanced Features for Enthusiasts
Overclocking Tools and BIOS
AI OC profiles in 2026 UEFI.
OC Tools Table
| Tool | Function |
| BIOS Flashback | Update: no CPU |
| LN2 Mode | Extreme cooling |
RAID and Storage Configurations
RAID 0/5 support via chipset.
2026 Exclusive Updates and Leaks
PCIe 6.0 Full Details
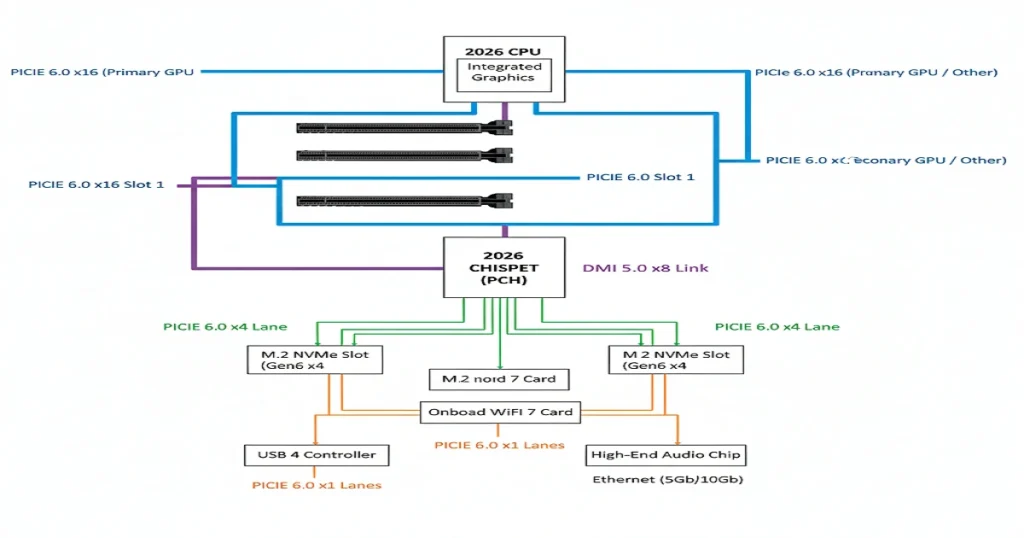
PAM4 signalling – first GPUs: RTX 6090 (Q3 2026).
PCIe Gen Table
| Gen | GT/s | GB/s (x16) |
| 5.0 | 32 | 256 |
| 6.0 | 64 | 512 |
DDR6 and Socket Longevity
JEDEC spec: 2.5V, on-die PMIC.
FAQs
1. What is a motherboard in a computer?
A motherboard is the main circuit board inside a computer. It connects and allows communication between all the important parts—such as the CPU, memory (RAM), storage drives, graphics card, and ports. It’s basically the central hub that lets all components work together.
2. What is the difference between a motherboard and a CPU?
Motherboard:
- The large board that holds and connects all components.
- Provides power and communication pathways.
- Cannot “think” or process data on its own.
CPU (Central Processing Unit):
- The “brain” of the computer.
- Performs calculations and runs instructions.
- Plugs into the motherboard.
In short: the motherboard is the platform; the CPU is the processor that does the work.
3. How to explain a motherboard to a child?
Imagine a motherboard like a big LEGO baseplate.
- All the other pieces (CPU, memory, drives) plug into it.
- It lets all the pieces talk to each other.
- Without the baseplate, the LEGO pieces would fall apart and couldn’t work together.
4. Can a PC run without a motherboard?
No.
A PC cannot run without a motherboard because:
- There would be no place to plug in the CPU, RAM, or power connections.
- There would be no circuits to let the parts communicate.
- The system wouldn’t be able to start at all.
Conclusion: Master Your Build
Motherboards aren’t just circuit boards; they’re the beating heart of your PC, deciding everything from smooth AI-powered workflows to blistering gaming performance. From the detailed anatomy of VRMs and PCIe 6.0 lanes to smart form factor choices and AI NPUs, choosing the right one means a future-proof build that lasts years without regrets.
In 2026, with DDR6 hitting 25,600 MT/s and PCIe 6.0 doubling speeds for RTX 6090 GPUs, now’s the time to invest in boards like ASUS ROG X870E or MSI MPG B860, which support Zen 6/AM6 longevity and Windows 12 AI features out of the box.