What Ram Will My Motherboard Support – How to Check in 2026
To know what RAM your motherboard will support, check its model name. Then see which DDR type, speed, and size it accepts on the maker’s website. Buy RAM that matches these details so your computer works fast and safe too.
When you search “What RAM Will My Motherboard Support”, it usually means you want a clear guide before buying new memory. Many people get confused because every motherboard accepts only certain RAM types, speeds, and sizes. A wrong choice can waste money or stop the PC from starting. In this guide, I will explain how to check your board’s model, read the right RAM details, and pick memory that fits perfectly. My goal is to give you simple steps that anyone can follow, even if you are new to computers, so you upgrade with confidence and avoid common mistakes.
What Is a Motherboard, and What Does It Do?
Your motherboard acts like the backbone of your computer. It connects your CPU, RAM, GPU, and storage into one system. Without it, no component can communicate properly. If you want to learn more about how motherboards function.
What Is RAM, and Why Does It Matter?
RAM (Random Access Memory) temporarily stores data your system needs to access quickly. Think of it as your computer’s short-term memory; the more you have, the smoother multitasking and gaming become. Curious about how motherboards manage memory?
Different Generations of RAM

Each generation of DDR memory, from DDR to DDR5, offers higher speeds, lower voltages, and improved efficiency. But they’re not interchangeable. DDR4 won’t fit in a DDR5 slot, and vice versa.
| Generation | Year | Pins (DIMM/SODIMM) | Notch Position |
| DDR | 2002 | 184 / 200 | Center |
| DDR2 | 2004 | 240 / 200 | Center |
| DDR3 | 2007 | 240 / 204 | Offset left |
| DDR4 | 2014 | 288 / 260 | Center |
| DDR5 | 2020 | 288 / 262 | Offset left |
RAM Form Factors: DIMM vs SODIMM
There are two main form factors:
- DIMM: used in desktop PCs.
- SODIMM: smaller modules for laptops.
Both serve the same purpose but differ in size and pin layout.
Understanding RAM Speed
RAM speed is measured in MHz or MT/s. A higher number means data moves faster between your CPU and memory. For example, 3200 MHz is standard for DDR4, while DDR5 often starts at 4800 MHz. Faster RAM improves gaming, video editing, and multitasking performance.
RAM Capacity and Density
Most desktop motherboards support two to four RAM slots. Higher-density modules like 16 GB or 32 GB per stick allow greater total capacity. Check your motherboard’s manual or the manufacturer’s website for the maximum supported memory.
How to Check What RAM Your Motherboard Supports
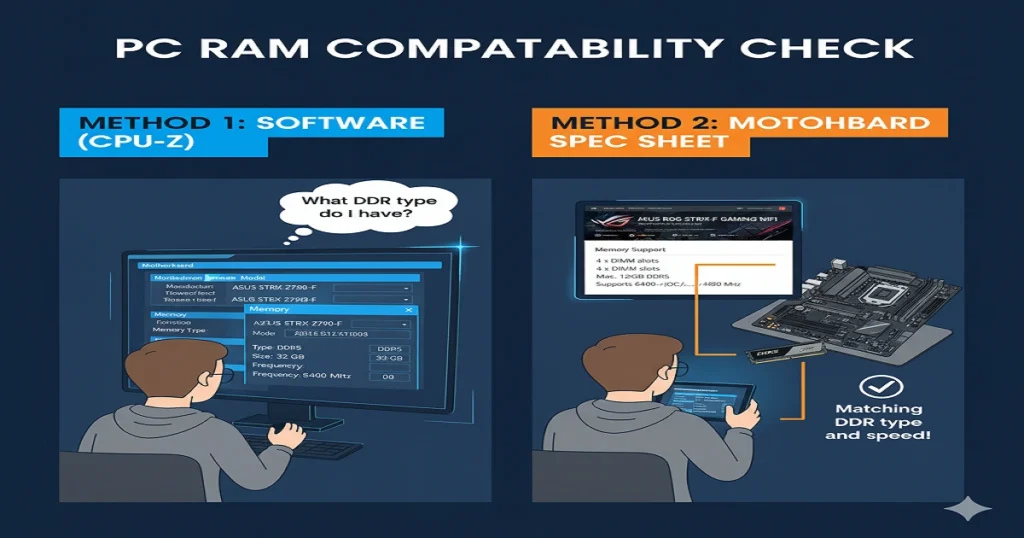
You can check in three ways:
- Manual Inspection: Look at the printed model name on your motherboard and search online.
- Software Tools: Use CPU-Z, Speccy, or Windows Task Manager to find the current RAM type and speed.
- Manufacturer Tools: Use compatibility checkers like Crucial System Scanner or Kingston Configurator to see the supported RAM list.
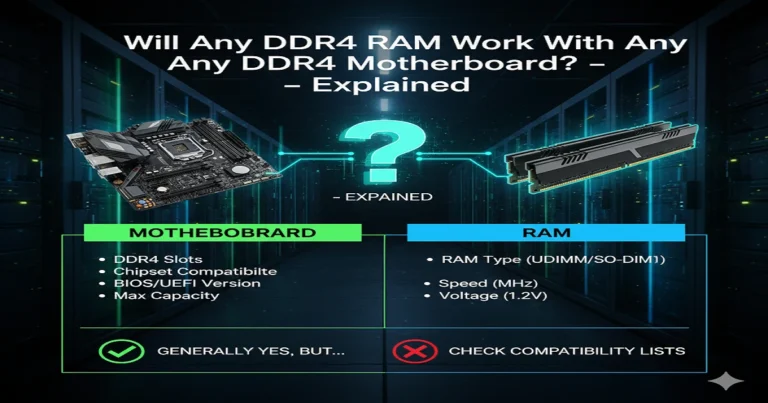
Why RAM and Motherboards Aren’t Always Compatible
Every motherboard supports only one RAM generation, DDR4 or DDR5, never both. Physical slot design prevents mismatched installation. Also, factors like RAM voltage, latency, and BIOS support play major roles in compatibility.
How to Determine Your DDR Generation
You can identify your DDR generation by:
- Check your motherboard manual.
- Running CPU-Z to see the current DDR type.
- Visiting the manufacturer’s site (e.g., ASUS, MSI, or Gigabyte) and reviewing your model’s memory QVL list.
Single, Dual, and Quad Channel Memory
Using two or four memory sticks improves data transfer speed due to the dual- or quad-channel architecture. Always install identical RAM sticks for stable performance. Avoid mixing different brands or speeds.
Understanding CAS Latency (CL) and Timings
CAS latency (CL) measures how fast the RAM can deliver data after a request. Lower latency means quicker performance. For example, CL16 is faster than CL18 when clock speeds are equal.
ECC vs Non-ECC RAM
Workstation motherboards often support ECC RAM (Error-Correcting Code), which automatically detects and fixes memory errors. Consumer motherboards, however, usually support non-ECC RAM because it’s cheaper and faster.
Buffered vs Unbuffered RAM
Registered (buffered) RAM is used in servers for stability under heavy loads. Unbuffered RAM is typical for desktops. Always verify this detail before purchasing; your motherboard manual will clarify it.
Voltage and Stability
Every DDR generation operates at a different voltage range. For instance, DDR4 runs around 1.2 V, while DDR5 can run at 1.1 V. Using the wrong voltage can cause boot failures or system instability.
How BIOS Updates Affect RAM Compatibility
A BIOS update can often expand compatibility for newer RAM models or improve stability at higher speeds. Before upgrading your memory, check for BIOS updates on your motherboard manufacturer’s website.
How to Install RAM the Right Way
- Power off your PC and unplug it.
- Open the case and locate the RAM slots.
- Align the notch and press down firmly until you hear a click.
- Close your case and boot the system.
- Enter BIOS to confirm the new memory is detected.
Common RAM Compatibility Mistakes
- Mixing DDR4 and DDR5 modules.
- Combining different frequencies (e.g., 2666 MHz and 3200 MHz).
- Installing sticks in the wrong slots (breaking the dual-channel setup).
- Ignoring BIOS updates before installation.
Using XMP or DOCP Profiles
XMP (Intel) and DOCP (AMD) are pre-configured profiles that allow your system to run RAM at its advertised speed. You can enable these profiles easily in BIOS for an instant performance boost.
Advanced Memory Features to Know
- EXPO Profiles (AMD) for fine-tuned memory speeds.
- Memory interleaving for optimised throughput.
- Dual-rank vs single-rank differences affecting performance.
- Thermal design for high-speed kits with heatsinks.
Laptop RAM vs Desktop RAM
Laptop RAM uses SODIMM modules, while desktops use DIMM. They are not interchangeable. Always check length and pin count before buying.
Future-Proofing Your Memory Upgrade
If you’re building a new PC, consider DDR5 for better longevity. It offers faster speeds and better efficiency. However, DDR4 is still a cost-effective choice for most users in 2025.
Troubleshooting RAM Detection Problems
If your system doesn’t detect new RAM:
- Reseat modules properly.
- Test each stick individually.
- Reset CMOS or update BIOS.
- Verify supported RAM list (QVL).
Memory Testing and Diagnostics
Use MemTest86 or the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to check for faulty RAM modules. Detecting bad memory early prevents crashes and data corruption.
FAQs:
How can I tell what RAM is compatible with my motherboard?
Check your motherboard’s manual or use tools like CPU-Z or the Crucial System Scanner to find the supported DDR generation, speed, and capacity.
Can I put 3200 MHz RAM in a 2400 MHz motherboard?
Yes, but it will automatically run at 2400 MHz, which is the maximum speed your motherboard can support.
How do I choose the right RAM for my motherboard?
Choose RAM that matches your motherboard’s DDR type, form factor (DIMM or SODIMM), and supported frequency range.
How to check if a motherboard is DDR3 or DDR4?
Use CPU-Z or Task Manager to check the DDR type, or visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website to view its detailed specifications.
Conclusion:
Knowing what RAM your motherboard will support makes upgrading easy and safe. Every motherboard works with only certain RAM types, speeds, and sizes. If you choose the wrong RAM, your computer may not start or run slowly. By checking your motherboard model and its memory details, you can pick the right RAM without any guesswork. Follow the simple steps in this guide to make sure your RAM fits perfectly. Using the correct RAM helps your PC run faster, open programs quickly, and work without problems. Always check carefully before buying for the best results.